|

by Paul Ratner
May 28,
2020
from
BigThink Website
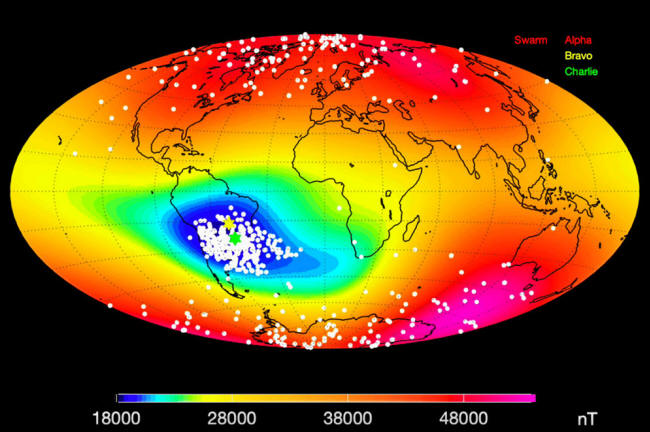
Satellite data shows
a new, eastern center emerging
in
the South Atlantic Anomaly.
ESA
A strange
weakness
in the Earth's
protective magnetic field
is growing and
possibly splitting,
shows data.
-
"The
South Atlantic Anomaly" in the Earth's magnetic field is
growing and possibly splitting, shows data.
-
The
information was gathered by the ESA's Swarm
Constellation mission satellites.
-
The
changes may indicate the coming reversal of the North
and South Poles.
A portion of the Earth's magnetic field, known as the "South
Atlantic Anomaly," is weakening and may be headed for a split, shows
new data.
The strange phenomenon is
also triggering technical problems in Earth-orbiting satellites.
Our planet's magnetic field is an important part of the defenses
that protect us from cosmic radiation and charged particles
streaming from the Sun.
The field is also the
reason compasses and GPS work.
It's generated by the
ocean of liquid iron in the planet's outer core, about 1800 miles
below our feet. The iron acts like "a spinning conductor in a
bicycle dynamo," explains the press release from the European
Space Agency (ESA), which carried out the research.
The iron's flow spawns
electrical currents that then generate the planet's ever-changing
electromagnetic field.
The liquid iron core behaves like a giant
magnet, causing the existence of the North and South poles.
The scientists were able to establish that the entire magnetic field
of the planet has diminished by 9 percent in its strength during the
past 200 years.
The "South Atlantic
Anomaly" segment, which stretches from Africa to South America, is
of particular concern.
Satellites from ESA's
Swarm Constellation mission, that looked into the anomaly detected a
strong weakening southwest of Africa, which points to the
possibility that the area would break into two different low points.
While the observed changes don't necessarily mean the Sun is about
to fry our planet or some similar calamity, it does indicate that
something is happening within the Earth's core.
This is what the agency
is hoping to figure out through further research.
One possibility:
the
north and south poles are about to switch positions, with the South
Atlantic Anomaly being the origin of the transformation (which
happens every 250,000 years or so).
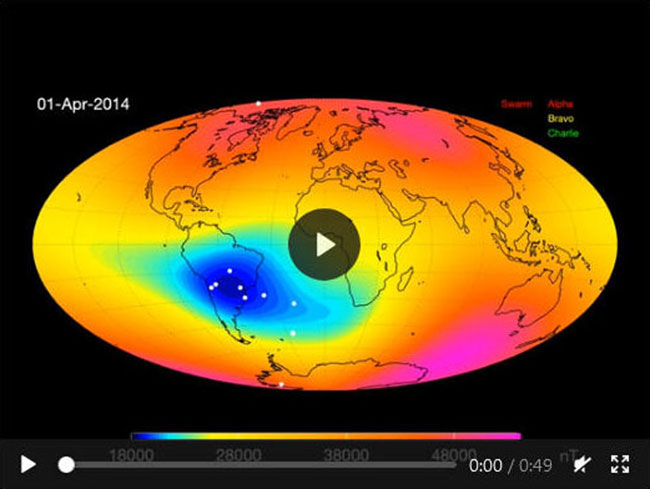
Click for video...
South Atlantic Anomaly impact radiation.
Credit:
ESA
Jürgen Matzka, a researcher into geomagnetism at the
GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, explained in a statement
that the new weak spot,
"has appeared over
the last decade and in recent years is developing vigorously."
He added that we're
fortunate to have the Swarm satellites studying the issue, while,
"the challenge now is
to understand the processes in Earth's core driving these
changes."
The weakness of the
magnetic field has occasionally caused the
International Space
Station and low-Earth orbit satellites to experience communication
and computer issues.
|