|

by Robby Berman
May 08, 2019
from
BigThink Website

The answer is surprisingly simple,
if cataclysmic.
-
A unique, tiny grain of stardust has provided a look at the early
universe.
-
Computer simulations point to a single neutron-star collision as a
significant source of heavy metals.
-
Gold is more than bling - it's in our neurons.
If you've got a thing for gold, you'd better have some money. Not
only is the precious metal beautiful, but the amount of it in the
universe is finite.
A new study (A
Nearby Neutron-Star merger explains the Actinide Abundances in the
Early Solar System) concludes that a single neutron star
merger some 300
parsecs away produced a significant amount of it.
"This means that in each of us we would find an eyelash worth of
these elements, mostly in the form of iodine, which is essential to
life," says one of the astronomers involved in the study,
Imre
Bartos at the University of Florida.
Gold in particular is pretty fascinating stuff - it can even be
argued that our individual existences depend on it, as astronomer
Michelle Thaller explains.
"There's gold
in your brain"
What it takes
to make gold
As Thaller notes, elements such as gold, platinum, plutonium and
others have atoms that are denser and thus heavier than iron atoms.
Gold, in particular, is about four times heavier, with each atom
containing many more protons and neutrons than iron. Such "heavy" elements are
primarily the product of "rapid neutron capture," or the
"r-process."
It takes place in
conditions of high neutron density and heat - think violent stellar
explosions - that allow a radioactive atomic nucleus to attract free
neutrons for an abnormally prolonged interval before its
radioactivity begins to decay.
This much as been agreed upon for some time.
Until now, though,
there's been a debate as to type of cosmic cataclysm responsible:
A tiny speck
of stardust tells the story
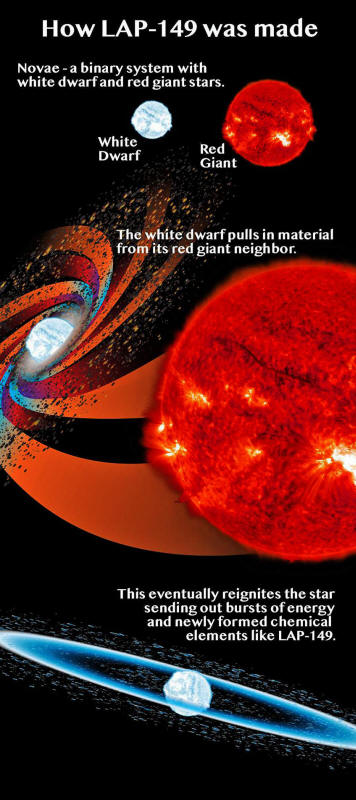
The basis of the researchers' conclusion is the composition of a
unique grain of stardust extracted from an Antarctic meteorite by
researchers at the University of Arizona, described last month in a
nature astronomy article (Laboratory
Evidence for Co-Condensed Oxygen- and Carbon-rich Meteoritic
Stardust from Nova Outbursts).
An electron-transparent
cross-section of grain LAP-149 - just 1/25,000 of an inch in size -
was examined to determine its composition.
Source
Lead author of the analysis study
Pierre Haenecour tells
UA
News,
"As actual dust from
stars, such presolar grains give us insight into the building
blocks from which our solar system formed."
The composition of
LAP-149 suggests formation in a nova.
Haenecour explains the
telltale clue was that it's so highly enriched in a carbon isotope
called 13C:
"The carbon isotopic
compositions in anything we have ever sampled that came from any
planet or body in our solar system varies typically by a factor
on the order of 50. The 13C we found in LAP-149 is enriched more
than 50,000-fold."
UA's
Tom Zega
says:
"If we could date
these objects someday, we could get a better idea of what our
galaxy looked like in our region and what triggered the
formation of the solar system."
Meanwhile, he notes,
"It's remarkable when
you think about all the ways along the way that should have
killed this grain," particularly during the violent creation of
our solar system.
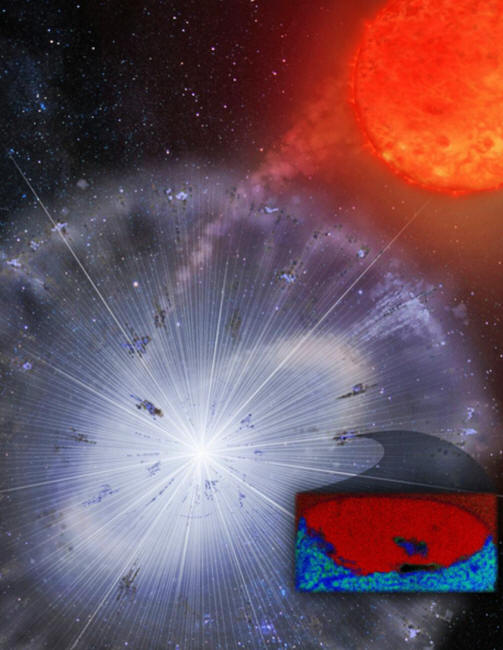

Image source:
UA News
|