|
Above images:
drawings from a flying object that it is thought the VRIL
Society assembly for traveling to
"the other side" |
Above image: small
flying system constructed in 1922 by the VRIL Society |
|

Junkers patent , dated 1910, of a strange flying machine
|

A sketch of the RFZ 2 |
Images of the RFZ prototypes
|

RFZ 2 test flight
|

In spite of
difficulties and deficiencies found in the construction of
the RFZ 2, this one was developed for a new model designated as
VRIL-1 |
|
Undergrounds constructions: they were built to manufacture
"strange" flying machines (VRIL),
having been used years later to build V-1 and V-2 bombs
|
Drawing: the great tunnels and galleries are well notorious as
it can be seen in this image |
|
There were several projects found by the Allies in the SS files,
when they occupied Berlin in 1945
|
|
At the beginning, the German technicians thought to apply
conventional "weaponry"
in these " flying machines", installing "Panzer" tank cannons.
|
|
The evolution of the VRIL and the
HAUNEBU was extremely fast thanks to the OVNI pieces
recovered at the Black Forest and in
Gdynia
|
|
 |
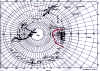 |
|
This map, cannot be
exhibited in Germany ...under prison penalty. Later on, the ban
was lifted by the German Parliament |
Territory occupied by
Germany on 1938 in Antarctica. Was given the name of
NEU-SCHABENLAND
|
|
The arrival of the
nazis to Antarctica and the "demarcation" of the occupied
territory (600.000 Km2), through drop-flags thrown by hydroplanes
|
|
 |

U-Boat submarine in Azores |
|
 |

U-Boat submarines in
Antarctica 1943 |
|
Some images of VRIL 7 and
VRIL 6 |
|
Details of bottom area:
VRIL 7
|
|

Detail of bottom area:
RFZ 5 |

Part of a project:
HAUNEBU III |

Part of ANDROMEDA
project : "flying cigar" transporter of different kind of
objects |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
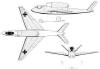
Arado Ar 65
(Year: DEC 1941 Speed.: 900 Km/h;
Altitude: 12.000 m;
Motors: Heinkel He 109)
|
Focke-Wulf Vorschlag 1
(Year: DEC 1942 Speed: 930 Km/h;
Altitude: 13.600 m;
Motors: BMW P 3302)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
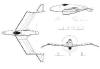
Henschel HS P 75
(Year: 1941 Speed.: 790 Km/h; Altitude: 12.000 m; Motors:
Daimler Benz DB 613 A/B) |
Henschel HS P 135
(Year: FEB 1945 Speed: 984 Km/h;
Altitude: 14.000 m;
Motors: Heinkel He S 011) |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
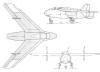
Blohm Voss BV P208/3
(Year: NOV 1944 Speed: 790 Km/h;
Altitude: 11.400 m;
Motors: Daimler Benz DB 603)
|
Junkers Ju EF 128
(Year: FEB 1945 Speed.: 990 Km/h;
Altitude: 13.700 m;
Motors: Heinkel He S 011) |
|
 |
 |
|
Gotha Go P60 C
(Year: FEB 1945 Speed: 930 Km/h; Altitude: 13.300 m;
Motors: Heinkel He S 011) |
|
Horten HIX
(Year: MAR 1945 Speed:
950 Km/h; Altitude: 16.000 m; Motors: Junkers Jumo 004 B-2)
|
|
Gotha P 60
(Year: JAN 1945 Speed: 915
Km/h; Altitude: 12.500 m; Motors: BMW 003 )
|
|

Horten XIIIb
( Year: 1944 Speed: 1200
Km/h; Altitude: 15.000 m; Motors: Heinkel He S 011 A-0 ) |
|