|
KV 47 (Siptah)
General Site Information
Structure: KV 47
Location: Valley of the Kings, East Valley, Thebes West Bank, Thebes
Owner: Siptah
Other designations:
Site type: Tomb
Description
KV 47 is located in the southwest branch
of the southwest wadi. The tomb consists of three gently sloping
corridors (B, C, D), followed by a chamber (E), a pillared chamber
(F), two subsequent corridors (G, H), and a chamber (I) that leads
through a passage with abandoned lateral cuttings for a burial
chamber (J1). These are followed by the actual unfinished burial
chamber J2, containing a granite sarcophagus. The entrance of the
tomb consists of a ramp with divided stairs. The tomb was left
unfinished. Only the first corridors and chamber were plastered and
decorated with scenes from the Litany of Ra (corridors B and C),
Book of the Dead (corridor C), Imydwat (corridor D), representations
of the deceased with Ra-Horakhty (corridor B), the sun disk on the
horizon (gate B) and winged figures of Ma'at (gate B, gate D).
Noteworthy features
Pillared chamber F is succeeded by two
corridors G and H instead of the usual corridor and stairway.
A cutting for the side of a burial chamber was begun in corridor J1,
but had to be abandoned when workers broke into KV 32. The burial
chamber J2 has no side chambers.
Site History
The tomb was the burial place of Siptah, and judging by the objects
in the tomb, of his mother, Queen Tiaa. The cartouches of the king
were erased, then restored with paint. Hartwig Altenmüller and
Anthony Spalinger believed the erasures took place at the end of
Dynasty 19, either for religious or political reasons.
KV 47 was reused during the Third Intermediate Period and robbed in
antiquity.
Edward Russell Ayrton was the first to excavate KV 47 in 1905.
Because of the safety risk posed by the bad condition of the rock,
he dug no further than chamber I. In 1912, Harry Burton resumed the
excavation and started to work in chamber F, clearing from this
point to burial chamber J. The tomb is currently under study by
Projekt MISR:
The mummy of Siptah was found in the tomb of Amenhetep II (KV 35) by
Victor Loret in 1898.
Dating
This site was used during the following period(s):
New Kingdom, Dynasty 19, Siptah
Third Intermediate Period, Dynasty 21 (Reburial of Siptah's
mummy in KV 35)
History of
Exploration
Ayrton, Edward Russell (1905): Discovery (made for Theodore M.
Davis)
Ayrton, Edward Russell (1905-1907): Excavation (conducted for
Theodore M. Davis)
Jones, Ernest Harold (1907): Epigraphy
Burton, Harry (1912-1913): Excavation
Carter, Howard (1922): Excavation (conducted around entryway A)
Supreme Council of Antiquities (1994): Conservation
Supreme Council of Antiquities (1994): Excavation
MISR Project: Mission Siptah-Ramses X (1999-): Conservation
MISR Project: Mission Siptah-Ramses X (1999-): Epigraphy
MISR Project: Mission Siptah-Ramses X (1999-): Excavation
Conservation
- Conservation history: During summer 1994, the
Supreme Council of Antiquities undertook a program to clear the
remainder of the tomb, repair damage and open it for tourists. In
addition to cleaning the painted relief and filling in gaps with
plaster, damaged gates D and E and their lintels were repaired. The
pillars in pillared chamber F had been damaged by past flooding and
were largely replaced by limestone blocks. Wood walkways were laid
over the floors (and on unexcavated debris in corridors G and H).
Glass panels were erected over the painted decoration and new
lighting was installed.
- Site condition: The first part of the tomb is well
preserved. Beyond corridor D, the walls have suffered of structural
damage. |
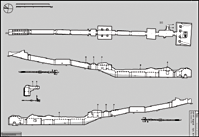
Printable Tomb Drawings
Axis in degrees: 172.04
Axis orientation: South
Site Location
Latitude: 25.44 N
Longitude: 32.36 E
Elevation: 185.16 msl
North: 99,410.433
East: 93,997.048
JOG map reference: NG 36-10
Modern governorate: Qena (Qina)
Ancient nome: 4th Upper Egypt
Surveyed by TMP: Yes
Measurements
Maximum height: 5.3 m
Minimum width: 1.79 m
Maximum width: 13.72 m
Total length: 124.93 m
Total area: 501.42 m²
Total volume: 1560.95 m³
Additional Tomb Information
Entrance location: Base of sloping hill
Owner type: King
Entrance type: Ramp
Interior layout: Corridors and chambers
Axis type: Straight
Decoration
Painting
Sunk relief
Categories of Objects Recovered
Human remains
Tomb equipment
Vessels
Writing equipment
|