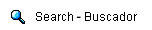|

by Phoebe Weston
November 13,
2018
from
DailyMail Website

Sunspots
have been absent for most of this year,
NASA scientists
say.
This is now the Earth's upper atmosphere
- the
thermosphere - responding.
Data comes from satellite which measures
changes in the
Earth's atmosphere.
It found the uppermost later of air
around the
planet is cooling and shrinking.
Changes high above Earth are unlikely
to impact
temperatures on our planet...
Global warmists
will eat crow for awhile while the earth cools and
it becomes obvious that the sun is the primary
determinant for earth's temperature.
The global warming meme is a fraud that does not
respect objective science.
Source
Lack of
Sunspots could bring a 'Space Age Record' for Cold Temperatures
above Earth in a matter of Months
A lack of sunspots could herald in a 'Space Age record' for cold
temperatures in the the Earth's upper atmosphere, a scientist has
warned.
The mercury could plummet in the thermosphere - a layer of gases
around 60 to 180 miles (100 to 300km) above the planet's surface -
as a result of the sun's inactivity.
Sunspots are not fully understood but they occur over regions of
intense magnetic activity as part of the 11 year solar cycle.
Ultra-violet radiation sent out across the cosmos from these
sunspots agitates particles in the Earth's atmosphere, causing them
to heat up.
Sunspots have been absent from the surface of the sun for most of
this year, causing the Earth's upper atmosphere to lose heat energy
as a result of the lack of agitation.
However, research has shown these changes high above Earth are
unlikely to have much of an impact on weather at the planet's
surface - including climate change.
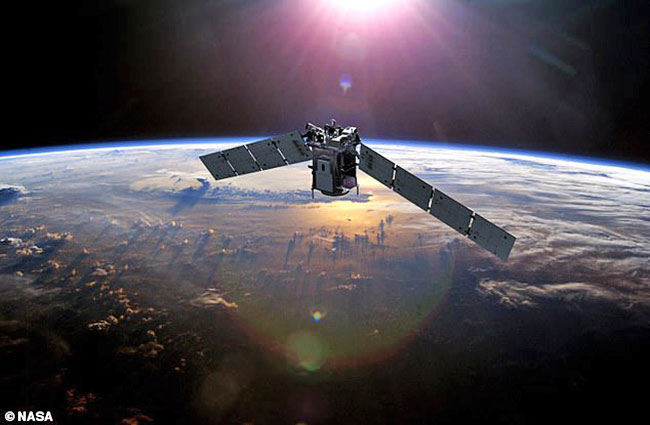

A lack of sunspots
could herald in a 'Space Age record'
for cold temperatures in the thermosphere,
a scientist has warned.
Researchers worked this out
using NASA's TIMED satellite (pictured)
which measures changes
in
the Earth's atmosphere.
(artist's impression)
'High above Earth's
surface, near the edge of space, our atmosphere is losing heat
energy', Dr Mlynczak told Dr Tony Phillips as part of an
in-depth feature in Space Weather.
'If current trends continue, it could soon set a Space Age
record for cold', he added.
The data comes from
NASA's
TIMED satellite, which measures
changes in the Earth's atmosphere.
It found the thermosphere is currently cooling and shrinking. They
found this out by using the SABER instrument on the TIMED satellite,
which monitors infrared emissions from carbon dioxide and nitric
oxide.
These two substances play an important role in the overall balance
of energy.
To keep track of its movements, researchers led by Dr. Martin
Mlynczav created the 'Thermosphere Climate Index' (TCI).
This number - which is expressed in Watts - shows how many heat
trapping molecules like carbon dioxide and nitric oxide are released
into space.
'SABER is currently measuring
33 billion Watts of infrared power from NO [nitric oxide]', Dr
Mlynczak said.
'That's 10 times smaller than we see during more active phases
of the solar cycle.'
It could set a record in
a 'matter of months' Dr Mlynczak said.
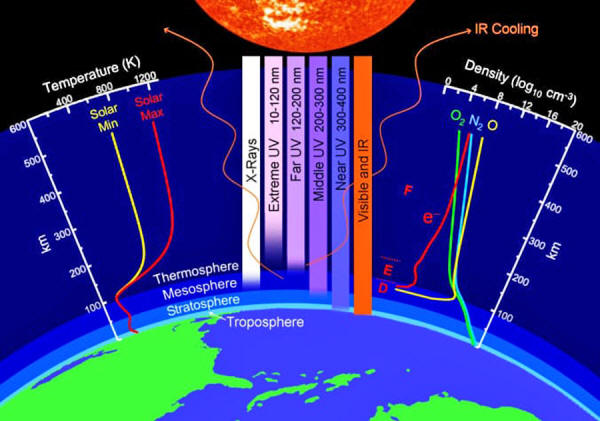
The thermosphere always cools off
during Solar Minimum as the sun's
ultraviolet output (pictured) drops sharply.
Sunspots have been absent for
most of this year and this is the Earth's
upper atmosphere responding,
Martin Mlynczak says
Solar activity tends to come and go in cycles lasting around 11
years and the star is currently experiencing a continuing period of
inactivity - as shown by a lack of sun spots.
The current Solar Minimum is causing dramatic changes in the
thermosphere. The thermosphere always cools off during
Solar Minimum as the sun's
ultraviolet output drops sharply.
The effects of solar minimum include Earth's upper atmosphere
cooling and shrinking slightly.
-
This can allow
space junk to accumulate in low Earth orbit.
-
An increase in
solar winds can also alter the chemistry of Earth's upper
atmosphere, which may trigger more lightning and aid in
cloud formation.
-
This can also
affect air travel, as an uptick means more radiation is able
to penetrate planes.
-
This means
passengers on long-haul flights may receive doses of
radiation similar to dental X-rays during a single trip, and
this puts flight crews in additional danger.

Solar activity tends to come and go
in
cycles lasting around 11 years
and the
star is currently experiencing a continuing
period
of inactivity - as shown by a lack of sun spots.
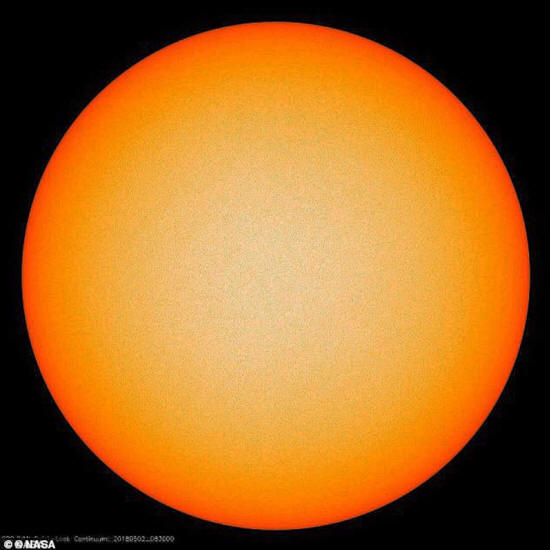
Earlier
this year, an eerily still surface of the sun
was
captured by cameras aboard NASA's SDO satellite
Earlier this year, an eerily still surface of the sun was captured
by cameras aboard NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)
satellite.
Showing a barren orange globe, the remarkable image it produced is
the result of a lack of sunspot activity in the star's magnetic
field. The sun was predicted to reach its 'solar minimum' low point
in 2019 or 2020, according to NASA's calculations.
Now, researchers say sunspots are vanishing faster than expected
and the current solar cycle may come to an end sooner than
previously thought.
Solar minimum may,
-
enhance the
effects of space weather
-
disrupt
communications and navigation
-
even cause space
junk to 'hang around', NASA says
WHY DO FEWER
SUNSPOTS CAUSE MORE PROBLEMS ON EARTH?
Lack of sunspot activity in the sun is due to a continuing period of
inactivity in the star's magnetic field.
As the sun moves through its 11-year cycle, it experiences active
and quiet periods known as the solar maximum and solar minimum.
As solar minimum approaches, certain types of activity - such as
sunspots and solar flares - will drop, but it's also expected to
increase long-lived phenomena.
This includes coronal holes, where fast moving solar winds are
created when the star's magnetic field opens up into space. This
happens more regularly as the sun's magnetic field becomes less
active.
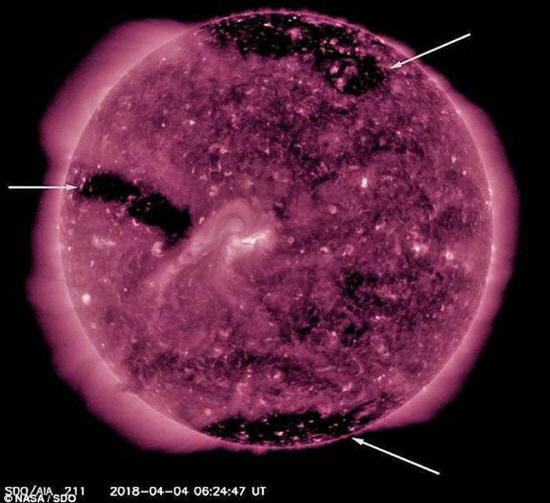
Strong solar winds
emanating from three massive 'holes'
on the
surface of the sun have begun
to
bombard Earth, scientists say.
Fast
moving solar winds are created where
the
star's magnetic field opens up into space,
captured as vast black regions
in this
satellite imagery.
Charged particles make their way out into the solar system through
these gaps and hit the atmosphere of our planet.
This can lead to a number of complications, including,
-
magnetic storms
which can result in power grid fluctuations
-
impact on
satellite operations
-
can affect
migratory animals
An increase in solar
winds can also alter the chemistry of Earth's upper atmosphere,
which may trigger more lightning and aid in cloud formation.
|