|
from
BigThink Website
and the
fine-structure constant.
Researchers dramatically improve the accuracy of a number
that connects
fundamental forces...
Physicists determined with tremendous accuracy the value of what's been called "a magic number" and considered one of the greatest mysteries in physics by famed scientists like Richard Feynman.
The fine-structure
constant (denoted by the Greek α for "alpha") shows the
strength of the electromagnetic forces between elementary particles
like electrons and protons and is utilized in formulas pertaining to
matter and light.
Scientists were able to improve its precision 2.5 times or 81 parts per trillion (p.p.t.), determining the value of the constant to be:
As the researchers write in their paper (Determination of the fine-structure constant with an accuracy of 81 parts per trillion), pinpointing the fine-structure constant with remarkable exactitude is not just a complex undertaking but holds crucial importance,
Getting a very precise value for a fundamental constant can help make more accurate predictions and open up new paths and particles, as physicists look to reconcile their science with the fact that they still don't fully understand,
The fine-structure constant, first introduced in 1916, describes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between light and charged elementary particles, like electrons and muons.
Confirming the constant with such accuracy further cements the calculations at the basis of the standard model of physics.
Other conclusions also
stem from this knowledge, like the fact that an electron has no
substructure and is indeed an elementary particle. If it could be
broken down any further, it would exhibit a magnetic moment that
would not conform to what was observed.
And amazingly,
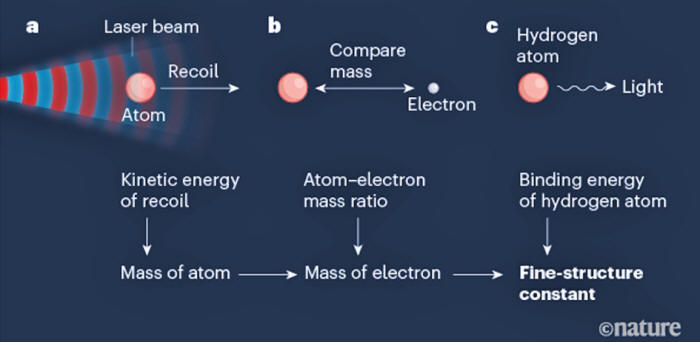
The process for measuring the fine-structure constant involved a beam of light from a laser that caused an atom to recoil. The red and blue colors indicate
the light wave's peaks and troughs, respectively.
This approach involves superimposing electromagnetic waves to cause an interference pattern, which is then studied for new information.
In the particular experiment to obtain the new fine-structure constant value, the scientists directed a laser beam at super-cooled rubidium atoms to make them recoil while absorbing and emitting photons.
By measuring the kinetic energy of the recoil, the scientists deduced the atom's mass, which was then used to figure out the electron's mass.
The constant α was
found in the next step, taken from the electron's mass and the
binding energy of a hydrogen atom, which was arrived at by
spectroscopy.
|