|

Special to World Science
1-8-6
from
Rense Website
A paper to appear in a scientific
journal claims a strange red rain might have dumped microbes from
space onto Earth four years ago.
But the report is meeting with a shower of skepticism from
scientists who say extraordinary claims require extraordinary
proof-and this one hasn't got it.
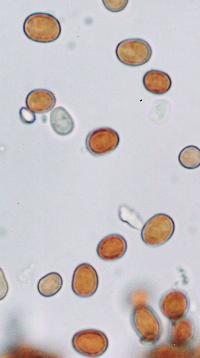
The particles at about 1000 times actual size (courtesy Godfrey
Louis).
The scientists agree on two points, though. The things look like
cells, at least superficially. And no one is sure what they are.
"These particles have much similarity with biological cells though
they are devoid of DNA," wrote Godfrey Louis and A. Santhosh Kumar
of Mahatma Gandhi University in Kottayam, India, in the
controversial paper.
"Are these cell-like particles a kind of alternate life from space?"
The mystery began when the scarlet showers containing the red specks
hit parts of India in 2001. Researchers said the particles might be
dust or a fungus, but it remained unclear.
The new paper includes a chemical analysis of the particles, a
description of their appearance under microscopes and a survey of
where they fell. It assesses various explanations for them and
concludes that the specks, which vaguely resemble red blood cells,
might have come from a meteor.
A peer-reviewed research journal, Astrophysics and Space Science,
has agreed to publish the paper. The journal sometimes publishes
unconventional findings, but rarely if ever ventures into generally
acknowledged fringe science such as claims of extraterrestrial
visitors.
If the particles do represent alien life forms, said Louis and
Kumar, this would fit with a longstanding theory called panspermia,
which holds that life forms could travel around the universe inside
comets and meteors.
These rocky objects would thus "act as vehicles for spreading life
in the universe," they added. They posted the paper online this week
on a database where astronomers often post research papers.
|
The shaded area represents the state of Kerala in India. (Courtesy
Nichalp) |
Louis and Kumar have previously posted other, unpublished papers
saying the particles can grow if placed in extreme heat, and
reproduce.
But the Astrophysics and Space Science paper doesn't
include these claims. It mostly limits itself to arguing for the
particles' meteoric origin, citing newspaper reports that a meteor
broke up in the atmosphere hours before the red rain.
John Dyson, managing editor of Astrophysics and Space Science,
confirmed it has accepted the paper.
But he said he hasn't read it
because his co-managing editor, the European Space Agency's Willem Wamsteker, handled it. Wamsteker died several weeks ago at age 63.
A paper's publication in a peer-reviewed journal is generally
thought to give it some stamp of scientific seriousness, because
scientists vet the findings in the process.
Nonetheless, the red
rain paper provoked disbelief.
"I really, really don't think they are from a meteor!" wrote Harvard
University biologist Jack Szostak of the particles, in an email.
And
this isn't the first report of red rain of biological origin, Szostak wrote, though it seems to be the most detailed.
Szostak said the chemical tests the researchers employed aren't very
sensitive.
The so-called cells are admittedly "weird," he added,
saying he would ask his microbiologist friends what they think they
are.
"I don't have an obvious explanation," agreed prominent
origins-of-life researcher David Deamer of the University of
California Santa Cruz, in an email. They "look like real cells, but
with a very thick cell wall. But the leap to an extraterrestrial
form of life delivered to Earth must surely be the least likely
hypothesis."
A range of additional tests is needed, he added. Louis agreed:
"There remains much to be studied," he wrote in an email.
The researchers didn't dispute the panspermia theory itself, which
has a substantial scientific following.
"Panspermia may well be
possible," wrote Lynn J. Rothschild of the NASA Ames Research Center
in Moffett Field, Calif., in an email. "I'm just not so sure that
this is a case of it."
Others viewed the study more favorably.
"I think more careful examination of the red rain material is
needed, but so far there seems to be a strong prima facie
[first-glance] case to suggest that this may be correct," said
Chandra Wickramasinghe, director of the Cardiff Centre for
Astrobiology at Cardiff University, U.K., and a leading advocate of
panspermia.
The story of the specks began on July 25, 2001, when residents of
Kerala, a state in southwestern India, started seeing scarlet rain
in some areas.
"Almost the entire state, except for two northern districts, have
reported these unusual rains over the past week," the BBC online
reported on July 30. "Experts said the most likely reason was the
presence of dust in the atmosphere which colours the water."
The explanation didn't satisfy everyone.
The rain "is eluding explanations as the days go by," the newspaper
Indian Express reported online a week later. The article said the
Centre for Earth Science Studies, based in Thiruvananthapuram,
India, had discarded an initial hypothesis that a streaking meteor
triggered the rain, in favor of the view that the particles were
spores from a fungus.
But,
"the exact species is yet to be identified. [And] how such a
large quantity of spores could appear over a small region is as yet
unknown," the paper quoted center director M. Baba as saying.
Baba
didn't return an email from World Science this week.
The red rain continued to appear sporadically for about two months,
though most of it fell in the first 10 days, Louis and Kumar wrote.
The "striking red colouration" turned out to come from microscopic,
mixed-in red particles, they added, which had "no similarity with
usual desert dust."
At least 50,000 kg (55 tons) of the particles have fallen in all,
they estimated.
"An analysis of this strange phenomenon further
shows that the conventional atmospheric transport processes like
dust storms etc. cannot explain" it.
"The red particles were uniformly dispersed in the rainwater," they
wrote. "When the red rainwater was collected and kept for several
hours in a vessel, the suspended particles have a tendency to settle
to the bottom."
"The red rain occurred in many places during a continuing normal
rain," the paper continued. "It was reported from a few places that
people on the streets found their cloths stained by red raindrops.
In a few places the concentration of particles were so great that
the rainwater appeared almost like blood."
The precipitation, the researchers added, had a,
"highly localized
appearance. It usually occur[ed] over an area of less than a square
kilometer to a few square kilometers. Many times it had a sharp
boundary, which means while it was raining strongly red at a place a
few meters away there were no red rain."
A typical red rain lasted
from a few minutes to less than about 20 minutes, they added.
The scientists compiled charts of where and when the showers
occurred based on local newspaper reports.
The particles look like one-celled organisms and are about 4 to 10
thousandths of a millimeter wide, the researchers wrote, somewhat
larger than typical bacteria.
"Under low magnification the particles look like smooth, red
coloured glass beads. Under high magnifications (1000x) their
differences in size and shape can be seen," they wrote.
"Shapes vary from spherical to ellipsoid and slightly elongated
These cell-like particles have a thick and coloured cell envelope,
which can be well identified under the microscope." A few had broken
cell envelopes, they added.
The particles seem to lack a nucleus, the core DNA-containing
compartment that animal and plant cells have, the researchers wrote.
Chemical tests indicated they also lacked DNA, the gene-carrying
molecule that most types of cells contain.
Nonetheless, Louis and Kumar wrote that the particles show
"fine-structured membranes" under magnification, like normal cells.
The outer envelope seems to contain an "inner capsule," they added,
which in some places,
"appears to be detached from the outer wall to
form an empty region inside the cell. Further, there appears to be a
faintly visible mucus layer present on the outer side of the cell."
"One characteristic feature is the inward depression of the
spherical surface to form cup like structures giving a squeezed
appearance," which varies among particles, they added.
"The major constituents of the red particles are carbon and oxygen,"
they wrote. Carbon is the key component of life on Earth. "Silicon
is most prominent among the minor constituents" of the particles,
Louis and Kumar added; other elements found were iron, sodium,
aluminum and chlorine.
"The red rain started in the State during a period of normal rain,
which indicate that the red particles are not something which
accumulated in the atmosphere during a dry period and washed down on
a first rain," the pair wrote.
"Vessels kept in open space also collected red rain. Thus it is not
something that is washed out from rooftops or tree leaves.
Considering the huge quantity of red particles fallen over a wide
geographic area, it is impossible to imagine that these are some
pollen or fungal spores which have originated from trees," they
added.
"The nature of the red particles rules out the possibility that
these are dust particles from a distant desert source," they wrote,
and such particles "are not found in Kerala or nearby place."
One easy assumption is that they "got airlifted from a distant
source on Earth by some wind system," they added, but this leaves
several puzzles.
"One characteristic of each red rain case is its highly localized
appearance. If particles originate from distant desert source then
why [was] there were no mixing and thinning out of the particle
collection during transport"? they wrote.
"It is possible to explain this by assuming the meteoric origin of
the red particles. The red rain phenomenon first started in Kerala
after a meteor airburst event, which occurred on 25th July 2001 near
Changanacherry in [the] Kottayam district. This meteor airburst is
evidenced by the sonic boom experienced by several people during
early morning of that day.
"The first case of red rain occurred in this area few hours after
the airburst... This points to a possible link between the meteor
and red rain. If particle clouds are created in the atmosphere by
the fragmentation and disintegration of a special kind of fragile
cometary meteor that presumably contain[s] a dense collection of red
particles, then clouds of such particles can mix with the rain
clouds to cause red rain," they wrote.
The pair proposed that while approaching Earth at low angle, the
meteor traveled southeast above Kerala with a final airburst above
the Kottayam district.
"During its travel in the atmosphere it must
have released several small fragments, which caused the deposition
of cell clusters in the atmosphere."
Alive or dead, the particles have some staying power, if the paper
is correct.
"Even after storage in the original rainwater at room
temperature without any preservative for about four years, no decay
or discolouration of the particles could be found."
|


