|

June 2019

Sir Francis Bacon first said in 1597, "Knowledge is
power", which has since become Google's unspoken
credo.
By controlling what gets to your eyes, ears and
mind, Google can control you and everyone else.
Mercola.com is the #1 alternative and health-related
site in the world, with a global rank of 6,335 of
most traffic sites, receiving over 13 million visits
per month.
48% of this traffic is from organic searches from
engines like Google. However, Mercola has also been
banned from Pinterest and shadow-banned by other
social media.
Source
Part 1
Google Crushes Traffic to a Website by 99%
by Joseph
Mercola
June 24, 2019
from
Mercola Website
Spanish version
Story
at-a-glance
-
This
year, we've seen an unprecedented push to implement
censorship across all online platforms, making obtaining and
sharing crucial information about health in general, and
vaccines in particular, increasingly difficult
-
Google's
June 2019 update, which took effect June 3, has effectively
removed Mercola.com from Google search results
-
When entering a health-related search word into Google, you
will no longer find Mercola.com articles in the search
results. The only way to locate Mercola articles is by
adding "Mercola.com" to the search word(s) in question
-
Mercola's fully referenced content has been at the top of
health search results for over 15 years
-
If
undesirable pages don't vanish automatically in the new
algorithm, Google's quality raters will manually manipulate
crowd-sourced relevance to bury the page or pages
Google buries Mercola
in their latest search engine update
Over the years, the government and business monopolies, including
the likes of Big Tech, have formed a global alliance hell-bent on
protecting and concentrating member profits.
The price for keeping
business going as usual is personal liberty and freedom of speech
that may impact these fascist government-industrial complexes.
The major industries colluding to take over the government and
government agencies include,
The leaders of these industries have organized strategies to buy off
politicians through lobbying and to capture regulatory agencies
through revolving door hiring strategies and paid-for media
influence through advertising dollars.
Big Tech has joined the movement, bringing in a global concentration
of wealth to eliminate competition and critical voices - voices that
bring awareness to the frightening future as our rights, freedoms
and competition erode into a fascist sunset, all disguised as a
means to protect you from "misinformation."
This year, we've seen an unprecedented push to implement censorship
across all online platforms, making it increasingly difficult to
obtain and share crucial information about health topics. If you've
been having difficulty finding articles from my website in your
Google searchers of late, you're not alone.
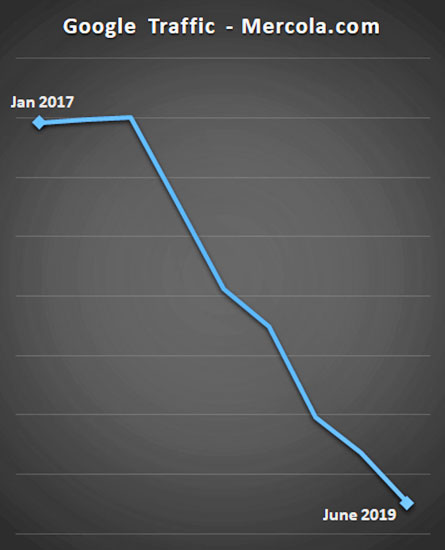
Google traffic to Mercola.com has plummeted by about 99% over the
past few weeks.
NB:
traffic as well to Bibliotecapleyades.net has plummeted by about 82%
The reason? Google's June 2019 broad core update,
which took effect June 3, 1 removed most Mercola.com pages from its
search results.
As reported by
Telaposts.com: 2
"The June 2019 Google Broad Core Algorithm Update impacted the
rankings of websites in Google's Search Engine Results Pages.
Several aspects of the algorithm were changed which caused some
sites to gain visibility and others to lose visibility.
Generally speaking, sites negatively impacted will see a drop in
rankings for many or all of important keywords or key phrases which
they used to rank well for…
The June 2019 Google Broad Core
Algorithm Update impacted sites across the web, however, I am
personally seeing the most impact on News and Health sites."
Mercola.com targeted in Google's latest core algorithm update
Now, any time you enter a health-related search word into Google,
such as "heart disease" or "Type 2 diabetes," you will not find
Mercola.com articles in the search results.
The only way to locate
any of my articles at this point is by searching for "Mercola.com
heart disease," or "Mercola.com Type 2 diabetes."
Even skipping the ".com" will minimize your search results, and
oftentimes the only pages you'll get are blogs, not my full
peer-reviewed articles.
Negative press by skeptics has also been
upgraded, which means if you simply type in my name none of my
articles will come but what you will find are a deluge of negative
articles voicing critiques against me in your searches.
Try entering
my name in Yahoo or Bing and you will see completely different
results.
As explained by Telapost, 3 a core update,
"is when Google makes
several changes to their main (core) algorithm."
In the past, Google
search results were based on crowd-source relevance. An article would
ascend in rank based on the number of people who clicked on it.
Traditionally, if you produced unique and high-quality content that
matched what people were looking for, you were rewarded by ranking
in the top of search results. You would find Mercola.com near the
top of nearly any health search results.
So, let's say one of my articles on diabetes was seventh on the page
for your search; if more people clicked on that link than, say, an
article listed in third or fifth place, my article would move up in
rank.
In a nutshell, Google search results were, at least in part,
based on popularity.
That's no longer the case. Instead, Google is now manually lowering
the ranking of undesirable content, largely based on Wikipedia's
assessment of the author or site.
Wikipedia's founder and anonymous editors are well-known to have
extreme bias against natural health content and authors.
Google also
contributes heavily to funding Wikipedia, and Wikipedia is near the
top of nearly all searches - despite the anonymous aspect of
contributors. Who better to trust than a bunch of unknown,
unqualified contributors?
Wikipedia's co-founder even admits these bad actors have made it a
"broken system." 4
Why would Google give such credibility to a
platform that even its own founder says is broken and overrun with
bad actors?
Google's new 'quality' rater guidelines are a death knell for experts
whose views threaten industry profits
Another major change was Google's 2019 quality rater guidelines,
5,6 released May 16.
What are these guidelines?
As explained by Telapost:
7
"Google hires 'quality raters,' people who visit websites and
evaluate their quality.
Their feedback doesn't directly impact your
site; it goes to engineers who update the Google algorithm in an
effort to display great websites to their users.
The guidelines give
us great insight as to what Google considers a quality web page."
One significant change: Google now buries expert views if they're
deemed "harmful" to the public.
As explained by The SEM
post: 8
"There has been a lot of talk about author expertise when it comes
to the quality rater guidelines… This section has been changed
substantially…
[I]f the purpose of the page is harmful, then
expertise doesn't matter. It should be rated Lowest!"
Google used to rank pages based on whether an author could prove
their expertise based on how many people visited a page or the
number of other reputable sites that linked to that page. No more.
As you may have noticed, we've stayed on top of this, even creating
a peer review panel of medical and scientific experts that review,
edit and approve most articles before they're published. This is in
addition to my own medical expertise as a board-certified physician.
My articles are also fully referenced, most containing dozens of
references to studies published in the peer-reviewed scientific
literature.
Alas, none of this now matters, as the very fact that
the information I present typically contradicts industry propaganda
places me in the lowest possible rating category.
Bait and switch
Different perspectives are essential to a healthy debate of ideas.
When our voices are censored humanity loses and fascism wins. Pinterest has banned me, Google has mostly erased my information and
many others are experiencing this same censorship.
What makes me so
dangerous to these industries that they need to censor me from those
looking for my information?
Google had the brilliant idea of utilizing crowd sourcing, providing
the best answers to your questions by pushing the most frequently
selected content to the top of the search results - a truly
democratic system to reward people for sharing information, and
helping you locate this information by essentially sharing the most
popular, highest quality content.
My information was frequently at the top of many health searches,
because many people like you found it to be the most valuable.
But
as Google's power grew to enormous proportions, the goal of
providing this service to you changed. The goal now is to become
even more powerful by uniting with other powerful industries and
government to force their beliefs on the masses and manipulate the
future itself.
Crowd sourcing has become crowd control.
Google began by giving you
everything you want so it can now take everything you have. Google
has changed from looking at users as customers and giving them what
they want, to making users custodians of their will - essentially
making you a host of a virus to carry out their agenda.
Google has become the ultimate puppet master, infecting people and
manipulating them without even knowing it.
Their true goal is to be
in complete control of all of us, directing our behavior - and
should we rebel, they also have partnered with the military to
create drones utilizing artificial intelligence to ensure resistance
will be defeated.
This is eerily reminiscent of many science fiction books and
productions, but we have proof of what Google is doing - and we
cannot go along with it. Google refers to the goal of controlling
humanity as "The Selfish Ledger," described in the video below.
Our
lives are being exploited by Google and other large tech companies,
and you have no idea how far they have come or where they are going.
The truth is, they can already predict and control your behavior.
Natural health and healing threaten drug and vaccine industry
profits
This sentence in the SEM Post article 9 cited earlier is key to
understanding what's going on:
"If the purpose of the page is
harmful, then expertise doesn't matter."
In other words, if a page
is deemed harmful to the public, it gets the lowest possible rating
regardless of expertise.
And if pages don't vanish automatically in
the new algorithm, quality raters will go in and manually manipulate crowd-sourced relevance to bury the page or pages.
Just what might Google and its industrial and government/military
allies deem "harmful"?
In short, pretty much anything that presents
views differing from the PR created by said allies, and that most
certainly includes alternative and holistic health, and articles
revealing the truth about toxic industries, including the drug and
vaccine industries.
Indeed, Telapost lists 10 Mercola.com as one of the biggest losers in
Google's June 2019 core algorithm update, along with other natural
health sites and Vimeo - a direct competitor to Google's Youtube
video platform.
The article also notes
that: 11
"In the QRG [quality rater guidelines], Google notes that raters
should conduct 'research on the reputation of the website or creator
of the main content.'
Later they say,
'…Wikipedia articles can help you learn about a
company and may include information specific to reputation, such as
awards and other forms of recognition, or also controversies and
issues.'
If a news style website has a poor reputation, factors on
their site could correlate with what Google is trying to push down
in search results."
I will delve into Wikipedia's role in this censorship movement in
Part 2 of this article, which will be published tomorrow.
Google is undoubtedly one of the largest and clearest monopolies in
the world. In fact, the company monopolizes several different
markets, including search and advertising.
Bing, its closest search
competitor, has just 2% of the market - hardly a significant threat
to Google's 90%. 12 Google also controls about 60% of the global
advertising revenue on the Internet .
So, with this core algorithm update, Google is very effectively
preventing a majority of people worldwide from learning about how to
protect and support their health, which is nothing short of an
attack on your civil liberties and right to pursue health and
happiness.
I've written about the dangers of monopolies within the drug and
agricultural industries on numerous occasions, but Google is without
a doubt the greatest monopoly that has ever existed on the planet,
and most people don't even realize it.
The technology giant has injected itself ever deeper into our
day-to-day lives, from childhood education to Android phones, to
patented meat substitutes 13 and health care.
Google's Internet
monopoly combined with its creepy personal information tracking and
sharing poses a very unique threat to public health, privacy and
well-being.
Anyone concerned about their health, food or environment and their
ability to obtain truthful information about any of those issues
needs to understand the role Google plays, and whose side Google is
really on.
I'll delve further into this in
part 2 far below.
Who are the Google
'quality' raters?
So, just who are these quality raters Google hires to decide who's
who and what's what, and manually rank pages higher or lower? Ars
Technica has written articles about the poor working conditions of
these raters.
In April 2017, senior tech culture editor for
Ars
Technica, Annalee Newitz, reported: 14
"Few people realize how much these raters contribute to the smooth
functioning act we call 'Googling.'
Even Google engineers who work
with rater data don't know who these people are. But some raters
would now like that to change.
That's because, earlier this month,
thousands of them received an e-mail that said their hours would be
cut in half, partly due to changes in Google's staffing policies.
Though Google boasts about its army of raters, the raters are not
Google employees.
Instead, they are employed by firms who have
contracted them to Google, full time, for years on end. These raters
believe that Google has reaped significant benefits from their labor
without ensuring their jobs are secure and stable.
That's why 10
raters came to Ars Technica to tell the story of what their lives
are really like."
At the time, Leapforce -
which was incorporated in 2008 15 - was one
of the largest companies supplying Google with raters.
Most raters
work from home and virtually everyone, including managers, use
online pseudonyms, preventing employees from knowing who they're
really working with.
"To get a task, raters log into Raterhub and see what's available.
Some days plenty of tasks exists; on others, a rater might wait
hours and be offered nothing…
A typical task takes anywhere from 30
seconds to 15 minutes, and the amount of time the rater can bill for
the task is pre-determined by Google," Newitz writes. 16
In 2017, the hourly pay for a rater ranged between $13.50 and
$17.40. 17
Effective June 1, 2017, Google raters working in the U.S.
could no longer bill for more than 26 hours a week, which meant
those working full-time (about 20% of Leapforce raters) were reduced
to part-time to minimize employee benefits.
In response to panicked workers, Leapforce founder and CEO Daren
Jackson 18 told the raters,
"this is not a change we are able to
control," and that the abolishing of full-time work was due to "risk
mitigation" related to "regulations."
According to Newitz, a new Google policy stipulated they wanted to
work with employee-based workforces, so to keep its contract,
Leapforce converted its raters from independent contractors to
employees.
It was very likely unlawful to have so many people
independently contracted for these positions in the first place.
However, Jackson told Newitz he couldn't convert his full-time
contractors to full-time employees,
"because Leapforce couldn't
afford health care for all of them," as required under the
Affordable Healthcare Act.
After speaking to Ars about their work
conditions, three of the raters were fired by Leapforce, Newitz
reported in a subsequent article. 19
Leapforce founder is a former Google employee
While Jackson claimed Leapforce had other clients beside Google
(which he would not name when asked by Ars Technica), Google
certainly appeared to be its largest.
It should come as no surprise
then that Jackson and Leapforce didn't just appear out of the blue.
In fact, as reported by Newitz, Jackson used to work for Google.
She writes: 20
"Jackson told Ars that he started Leapforce in 2008 after quitting
Google, where he had been working on a project called EWOQ.
EWOQ is
the precursor to Raterhub, though its origins are shrouded in
secrecy. We do know that, as early as 2004, Google had a quality
rater tool... At that time, raters were hired directly by Google...
But by the time Google purchased the website Raterhub.com in 2012,
all of Google's raters were coming from contracting companies like
-
Leapforce
-
Lionbridge
-
Appen
-
ZeroChaos
Many of Leapforce's
raters still call the tool they use at Raterhub 'EWOQ,' though one
told me that they have no idea why, nor what it stands for."
In essence, the separation between Leapforce and Google appears to
have been little more than a legal fiction that shielded Google from
any legal liabilities for the way this workforce was treated.
In a subsequent article, 21 published May 2, 2017, Newitz pointed out
that Jackson had just created yet another rating company called
RaterLabs, 22 and was in the process of transferring raters from Leapforce to RaterLabs, but at reduced pay rates.
As reported by Newitz in a third article, 23 published December 1,
2017, Leapforce/RaterLabs were ultimately acquired by a top
competitor, Appen. 24
She also reported that several Leapforce raters
had filed complaints with employee rights groups.
Two of the raters
fired after speaking to Ars Technica filed complaints with the
National Labor Relations Board. Both cases were reportedly settled.
Google is not an independent actor in its censorship movement
While some argue that Google, being a private company, has the right
to do whatever it wants, even if that means creating algorithms that
censor important and relevant news and health insights while
manually burying "undesirable" pages to protect the profits of its
advertisers and other financial stakeholders.
However, being one of the biggest monopolies in the world, one could
argue Google has really become more of a utility (like gas, water
and electric utilities), and as such has a responsibility to serve
the people.
In fact, last year, U.S. House Rep. Steve King, R-Iowa,
suggested Google and Facebook be turned into, and regulated as,
public utilities. 25
After all, if you want to find an answer on the web what do you do?
You Google it, you don't just "search." Google worked for many years
to earn your trust, but it was just setting a trap to twist that
trust into powerful control.
Unfortunately, even if such an idea were to gain traction (which it
has not), it still wouldn't solve the problem, as Google is not
acting independently, but rather is merely fulfilling a role within
a much larger complex that includes the U.S. government, its
military and national security apparatus, as well as several of the
wealthiest and most powerful industries on the planet.
I'll delve
into these issues in part 2 far below.
All of these "partners" have a vested interest in censoring
information addressed by yours truly on a daily basis:
Again, as explained earlier, Google's latest core algorithm update
and quality rater guidelines bury all of this information, favoring
instead information relayed by sites that are either part of this
industrial-technological-military-government complex, or that peddle
the desired talking points.
It doesn't matter that I'm reporting on and referencing publicly
available peer-reviewed research and have a whole panel of medical
and scientific experts reviewing much of the information, because
the science I highlight is the science industry doesn't want you to
see.
Few are ever going to take the time to dig up these studies even
though they're readily available, and thus by censoring me and other
online sources like myself, the
industrial-technological-military-government complex's task of
social engineering is significantly simplified.
The information we share about,
...and
other dangerous additives are prime targets for censorship for the
simple reason that when you take control of your health, they LOSE
control over you.
By being informed, you take their power over you
away from them.
What can you do?
I have been writing about Google for years because I knew this day
would come.
June 03, 2019, Google predictably removed my website and
several other health sites from its search results.
It's a wakeup call for everyone, and now more than ever we must work
together to share this information with others by word of mouth, by
text and email. We have built in simple sharing tools at the top of
each article so you can easily email or text interesting articles to
your friends and family.
My information is here because all of you support and share it, and
we can do this without Big Tech's support.
It's time to boycott and
share!
Here are a few other suggestions:
-
Become a subscriber to my newsletter and encourage your friends
and family to do the same. This is the easiest and safest way to
make sure you'll stay up-to-date on important health and
environmental issues.
NB:
Become a subscriber too, to
Biblioteca Pleyades newsletter.
-
If you have any friends or relatives that are seriously interested
in their health, please share important articles with them and
encourage them to subscribe to our newsletter.
-
Use the internal Mercola.com search engine when searching for
articles on my site. Nearly all major search websites except Yahoo!
and Bing still use Google as their primary engines and have their
own privacy issues. Then you have sites like StartPage and
DuckDuckGo, which provide greater privacy than Google, but rely on
Google's search results.
NB:
Use the internal
Biblioteca Pleyades search engine
when searching for articles in B. Pleyades.
-
Boycott Google by avoiding any and all Google products:
-
Stop
using Google search engines. Alternatives include
DuckDuckGo 26 and
Startpage 27
-
Uninstall Google Chrome and use
Brave or
Opera browser instead,
available for all computers and mobile devices. 28 From a security
perspective, Opera is far superior to Chrome and offers a free VPN
service (virtual private network) to further preserve your privacy
-
If you have a Gmail account, try a non-Google email service such
as
ProtonMail, 29 an encrypted email service based in Switzerland
-
Stop
using Google docs. Digital Trends has published an
article suggesting a number of alternatives 30
-
If you're a high school student, do not convert the Google
accounts you created as a student into personal accounts
-
Sign the
"Don't be evil" petition created by
Citizens Against
Monopoly
Sources and References
1
Twitter.com Google Search Liason June 3, 2019
2, 3, 10, 11
Telapost, The June 4, 2019 Google broad core algorithm
update
4
150sec.com May 23, 2019
5, 8, 9 The
SEM Post.com May 17, 2019
6, 7 Telapost
2019 Google quality rater guidelines
12
CBS News May 21, 2018
13
BBC News August 5, 2013
14, 16, 17, 20
Arstechnica.om April 27, 2017
15
Corporationwiki.com Daren Jackson company: Leapforce
18
Crunchbase.com Daren Jackson
19, 23
Arstechnica.com December
1, 2017
21
Arstechnica.com May 2,
2017
22
Corporationwiki.com Daren
Jackson company: Raterlabs
24
Passleapforceexam.com November 30, 2017
25
Tech Crunch July 17, 2018
26
Fast Company, Inside DuckDuckGo
27
Startpage.com
28
Opera Browser
29
ProtonMail
30
Digital Trends April 28,
2017
Part 2
Google
raters use Wikipedia for 'expertise' and 'trustworthiness'
by Joseph
Mercola
June 25, 2019
from
Mercola Website
Story at-a-glance
-
Google's June 2019 broad core algorithm update, which
started taking effect June 3, and its updated quality
rater guidelines have effectively removed Mercola.com
from Google search results
-
When
entering a health-related search word into Google, you
will no longer find Mercola.com articles in the search
results. The only way to locate Mercola articles is by
adding "Mercola.com" to the search word(s) in question
-
One
of the primary sources Google's quality raters are
instructed to use when assessing the expertise,
authoritativeness and trustworthiness of an author or
site is Wikipedia
-
Wikipedia is censoring information and crafting
narratives to benefit certain groups; it started
censoring information and blocking editors shortly after
its inception. Co-founder Larry Sanger calls Wikipedia
"a broken system"
-
Together with Amazon, Apple and Facebook, Google is
amassing "an army" of lobbyists - 75% of which have
served in government or on political campaigns - to
ensure survival as antitrust investigations into the
four companies get underway
In Part 1 far above,
it was
discussed the effects Google's June 2019 broad core algorithm update
and updated quality rater guidelines is having on traffic to this
site.
As mentioned in Part 1, Google's "quality raters" are now manually
lowering the ranking of undesirable content and buries even expert
views if they're deemed "harmful" to the public.
Google raters
use Wikipedia for 'expertise' and 'trustworthiness'
One of the primary sources Google's quality raters are instructed to
use when assessing the expertise, authoritativeness and
trustworthiness of an author or website is Wikipedia, "the free
encyclopedia."
Excerpts from my
Wikipedia page read: 1
"Joseph Michael
Mercola (born 1954) is an alternative medicine proponent,
osteopathic physician, and Web entrepreneur, who markets a
variety of controversial dietary supplements and medical devices
through his website, Mercola.com...
Mercola criticizes many aspects of standard medical practice, such
as vaccination and what he views as overuse of prescription drugs
and surgery to treat diseases.
On his website mercola.com, Mercola and colleagues advocate a number
of unproven alternative health notions including homeopathy, and
anti-vaccine positions...
Mercola's medical claims have been
criticized by business, regulatory, medical, and scientific
communities."
RationalWiki, the stated purpose of which is to analyze and refute
"pseudoscience and the anti-science movement" presents me as: 2
"[A] member of the right-wing quack outfit Association of American
Physicians and Surgeons.
Mercola advocates and provides a forum for
many classic crank medical ideas, such as vaccine hysteria and the
belief that modern (sorry, "allopathic") medicine kills more people
than it helps.
His website is a veritable spring of pseudoscience,
quackery, and logical fallacies. He is also a promoter of the idea
of an AMA/Big Pharma/FDA conspiracy."
It comes as no surprise then that Mercola.com is listed as one of
the biggest losers in Google's June 2019 core algorithm update. 3
Since its implementation, Google traffic to my site has dropped by
approximately 99%, as no Mercola.com pages will now appear in search
results using keywords only.
To have any chance of finding my articles using Google search, you
have to add "Mercola.com" to your search term (example: "Mercola.com
heart disease" or "Mercola.com Type 2 diabetes").
Even skipping the
".com" will minimize relevant search results.
Wikipedia
isn't what it pretends to be
How can Wikipedia be a primary authority of credibility when the
editors are anonymous and uncredentialed?
Wikipedia has bizarre
policies, including to never use a primary source for information -
only 'secondary' sources are considered applicable for sourcing
information.
In the 2016 Full Measure
article 4 "The Dark Side of Wikipedia," investigative
journalist Sharyl Attkisson
exposed the fact that Wikipedia is
censoring information and crafting narratives
to benefit certain
groups:
"The promise of accurate, neutral articles and privacy for
contributors is often just a mirage, according to two insiders. They
say they've been left battle-scarred after troubling personal
encounters with the world's most popular encyclopedia.
It's billed
as 'the encyclopedia anyone can edit.' But for many, it's the
opposite."
While Google's censoring of content is a more recent phenomenon,
Wikipedia has been censoring information and blocking editors since
the beginning.
According to Greg Kohs,
one of the insiders
interviewed by Attkisson, about 1,000 users are blocked from the
platform on any given day. 5
Attkisson writes:
"When Kohs ran afoul of Wikipedia, he was drawn into an unseen
cyberworld. One where he says volunteer editors dole out punishment
and retaliation, privacy is violated and special interests control
information."
As reported by Attkisson, Wikipedia is often edited by people with a
very specific agenda, and anyone who tries to clarify or clear up
inaccuracies on the site is simply blocked.
The reality is a far cry
from Wikipedia's public promise, which is to provide readers with
unbiased information.
'Inmates
running the asylum'
Even Lawrence (Larry) Sanger, who co-founded Wikipedia in 2001,
bailed ship the very next year, 6 saying "trolls sort of
took over" the site, that,
"The inmates started running the asylum,"
7 and that "In some fields and some topics, there are
groups who 'squat' on articles and insist on making them reflect
their own specific biases." 8,9
Earlier this year, Sanger told 150Sec he and co-founder Jimmy Wales
tried to "figure out how to rein in the bad actors."
He admits they were never
able to devise a good strategy for that, and as a result,
"Wikipedia
is a broken system." 10,11
Full Measure reports:
12
"In Wikipedia's
world, the ruling authorities are the hundreds of volunteer
editors who've reached the most powerful editing status. They're
called 'administrators,' known only by their pseudonyms or user
names.
They always win the edit wars.
Sharyl: The more edits you make, the longer you've been making
them, the more power you're going to have?
Kohs: Yes.
But what happens when powerful editors improperly control
content?
Kohs: You'll
have different people with a particular scientific point of view
and they'll edit and modify Wikipedia so that its articles kind
of reflect that point of view...
Two trusted Wikipedia officials were exposed running businesses
that covertly edited Wikipedia for PR clients.
Interests for
Sony, the CIA, the Vatican, Barack Obama and John McCain all
reportedly have been caught secretly editing their own Wikipedia
pages to their advantage.
And anonymous Wikipedia editors maintain a stranglehold on
selected topics… One study found mistakes in nine out of ten
Wikipedia medical entries.
Millions of dollars
can depend on how an idea or product is portrayed within the
computer pages...
Kohs: When you read Wikipedia, you have to be aware that the
people who are writing it, who don't identify themselves, who
don't necessarily have any credentials to be writing in the
subject matter that they've chosen to write in, are very often
pushing an agenda."
Wikipedia is controlled by special interests
Three years later, May 25, 2019, Attkisson wrote 13 about
her own struggles with Wikipedia.
She also discussed it in a TedX
talk (above) on astroturf tools.
"My own battle with
Wikipedia included being unable to correct provably false facts
such as incorrect job history, incorrect birth place and
incorrect birth date," she writes. 14
"What's worse is that
agenda editors related to pharmaceutical interests and the
partisan blog Media Matters control my Wikipedia biographical
page, making sure that slanted or false information stays on it.
For example, they falsely refer to my reporting as
'anti-vaccine,' and imply my reporting on the topic has been
discredited.
In fact, my vaccine and medical reporting has been recognized by
top national journalism awards organizations, and has even been
cited as a source in a peer reviewed scientific publication.
However, anyone who tries to edit this factual context and
footnotes onto my page finds it is quickly removed.
What persists on my page, however, are sources that are
supposedly disallowed by Wikipedia's policies. They include
citations by Media Matters, with no disclosure that it's a
partisan blog.
Another entity quoted on my Wikipedia biographical page to
disparage my work is the vaccine industry's Dr. Paul Offit.
But
there's no mention of the lawsuits filed 15 against
Offit for libel (one prompted him to apologize and correct his
book), or the fact that he provided false information about his
work and my reporting to the Orange County Register, which later
corrected 16 its article.
Obviously, these
facts would normally make Offit an unreliable source, but for
Wikipedia, he's presented as if an unconflicted expert. In fact,
Wikipedia doesn't even mention that's Offit is a vaccine
industry insider who's made millions of dollars off of
vaccines...
The powerful interests that 'watch' and control the pages make
sure Offit's background is whitewashed and that mine is subtly
tarnished.
They will revert or change any edits that attempt to
correct the record."
Sanger believes the
solution to the Wikipedia problem is a decentralized blockchain
system where edits are approved by a community.
This is how Everipedia, which Sanger joined in 2017, is run.
He told 150Sec:
17
"Since last July, every edit to Everipedia has had to be approved by
the community of IQ token-holders. 'IQ' is the Everipedia token, or
cryptocurrency. If someone uploads nonsense or copyrighted text, we
downvote it.
This already provides for a layer of editorial
oversight that Wikipedia lacks.
We have barely even started to explore what will be possible when
there is no centralized control of editorial policy, when editorial
decisions are made according to various smart contract-driven
systems, and when participation in the system is remunerated by the
system itself."
Wikipedia co-founder openly hostile against holistic medicine
As early as 2010, the Alliance for Natural Health pointed out the
impossibility of finding,
"information that isn't heavily biased
toward conventional medicine and the pharmaceutical industry" on
Wikipedia, 18 and matters certainly have not improved in
the years since.
If anything, they've gotten much, much worse.
Still, even back then, ANH gave several examples of the blatant
censorship of holistic medicine.
As just one example, the president
of the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine was prevented from
posting positive information about anti-aging derived from the
academy's own research.
From where I stand, it seems Sanger's co-founding partner, Wales, is
part of the problem. Wales is openly hostile against holistic
medicine, and in 2014 rejected a Change.org petition to bring in
more positive discussion of holistic medicine on Wikipedia.
As
reported by Business Insider: 19
"The petition, which has nearly 8,000 supporters, calls for people
to stop donating to Wikipedia in response to what it called 'biased,
misleading, out-of-date, or just plain wrong' information about
holistic approaches to healing."
Wales' response: 20
"No, you have to be kidding me...
Wikipedia's policies around this
kind of thing are exactly spot-on and correct. If you can get your
work published in respectable scientific journals - that is to say,
if you can produce evidence through replicable scientific
experiments, then Wikipedia will cover it appropriately.
What we
won't do is pretend that the work of lunatic charlatans is the
equivalent of 'true scientific discourse'. It isn't."
Google funds Wikipedia
Considering Wikipedia's history of bias and its incredibly effective
blocking of opposing views, no matter how factual, it's not
surprising that Wikipedia is Google's chosen arbiter of expertise
and credibility.
It also means the whole "quality rating" system
Google has set up is rotten from the ground up, as its quality
raters are instructed to base their quality decisions on an already
biased source.
As reported by Tech Crunch, 21
in January 2019, Google
donated $2 million to Wikimedia Endowment, Wikipedia's parent
organization, and another $1.1 million to the Wikimedia Foundation.
Together, Wikipedia and Google are also working on Project Tiger,
which will expand Wikipedia's content into more languages.
In a blog
post, Google president Jacquelline Fuller wrote: 22
"While efforts to empower editors will help them continue to add
more information and knowledge to the web, we also aim to support
the long-term health of the Wikimedia projects so they are available
for generations to come."
In other words, biased Wikipedia editors will receive even more
support, and with the backing and injections of funding from Google,
Wikipedia will be in an excellent position to further the
stranglehold on natural health in years to come.
Antitrust
complaints ignored
As mentioned in part 1 far above, Google is the largest monopoly in the world.
Yet while the European Union successfully raised antitrust charges
against Google, resulting in a $2.7 billion fine - and this despite
the revolving door between Google and EU policy advisers 23
- the U.S. has continued to look the other way.
The Federal Trade Commission investigation that took place during
the Obama administration, for example, resulted in no formal action
whatsoever. 24
One possible reason for this, Music
Technology Policy 25 suggested back in 2016, could be
because Google managed to install one of its former lawyers in the
U.S. Department of Justice's antitrust division, thereby protecting
the company's interests.
The revolving door swings both ways, of course. In 2007, Google paid
Makan Delrahim - a lawyer and current deputy assistant attorney
general of the DOJ's antitrust division - $100,000 26 to
lobby for the approval of its acquisition of DoubleClick, which was
under antitrust review. 27,28
Sen. Elizabeth Warren,
D-Mass., has also pointed out that Delrahim lobbied on behalf of
Apple in 2006 and 2007.
As reported by The New York Times 29 and The Verge,
30 Delrahim,
"is now facing pressure to recuse himself if the
Justice Department pursues an investigation..."
A study 31
by Public Citizen published May 23, 2019, found a whopping 59% of
FTC officials entered into financial relationships with technology
companies after leaving the agency.
All of this brings us to the issue of monopolization and the
corruption that inevitably follows. 32
It is very clear
that there is no company operating in breach of antitrust rules as
blatantly as Google. Absolute power corrupts absolutely, and this
adage certainly fits when describing Google.
As reported by The
Washington Post in 2017: 33
"Google has
established a pattern of lobbying and threatening to acquire
power.
It has reached a
dangerous point… The moment where it no longer wants to allow
dissent...
Once you reach a pinnacle of power, you start to believe that
any threats to your authority are themselves villainous and that
you are entitled to shut down dissent. As Lord Acton famously
said, 'Despotic power is always accompanied by corruption of
morality.' Those with too much power cannot help but be evil.
Google, the company dedicated to free expression, has chosen to
silence opposition, apparently without any sense of irony…
[I]n
recent years, Google has become greedy about owning not just
search capacities, video and maps, but also the shape of public
discourse."
Google
recruits law professors to defend its corporate views
To help sway public opinion and policy, Google has also recruited
law professors to back up and promote its views.
According to a 2017
Campaign for Accountability report, 34 Google has paid
academics in both the U.S. and Europe millions of dollars to
influence public opinion and policymakers alike. 35,36
This includes funding research papers,
"that appear to support the
technology company's business interests and defend against
regulatory challenges such as antitrust and anti-piracy."
Some of
these academics have not declared the source of their funding, even
though payments have reached as high as $400,000. 37
As noted by The Times:
38
"On one occasion Eric
Schmidt, Google's former chief executive, cited a Google-funded
author in written answers to Congress to back his claim that his
company was not a monopoly - without mentioning that it had paid
for the paper…"
'Tech giants amass
lobbying army'
Power can be assessed by looking at lobbying expenditures and Google
is leading the pack when it comes to corporate spending on lobbying
- efforts primarily aimed at eliminating competitors and gaining
power over others.
Google also appears to
take full advantage of its power over organizations that it helps
fund, which is one reason to be suspicious of its donations to
Wikipedia.
According to a June 5, 2019, article 39 in The New York
Times,
"[F]our of the
biggest technology companies are amassing an army of lobbyists
as they prepare for what could be an epic fight over their
futures."
The four companies in
question are,
-
Google
-
Facebook
-
Amazon
-
Apple
Combined, these
four tech giants spent $55 million on lobbying in 2018 - double what
they spent in 2016.
The New York Times
continues: 40
"As they have tracked
increasing public and political discontent with their size,
power, handling of user data and role in elections, the four
companies have intensified their efforts to lure lobbyists with
strong connections to the White House, the regulatory agencies,
and Republicans and Democrats in Congress.
Of the 238 people registered to lobby for the four companies in
the first three months of this year… about 75 percent formerly
served in the government or on political campaigns…
Many worked
in offices or for officials who could have a hand in deciding
the course of the new governmental scrutiny.
The influence campaigns encompass a broad range of activities,
including calls on members of Congress, advertising, funding of
think-tank research and efforts to get the attention of
President Trump...
Earlier this week, the
threat of government action became more real, driving down their
stock prices. The House Judiciary Committee announced a broad
antitrust investigation into big tech.
And the two top
federal antitrust agencies agreed to divide oversight over
Apple, Amazon, Facebook and Google as they explore whether the
companies have abused their market power to harm competition and
consumers...
The industry's troubles mean big paydays for the lawyers, political
operatives and public relations experts hired to ward off
regulations, investigations and lawsuits that could curtail the
companies' huge profits."
Going forward, the DOJ will be investigating Google and Apple -
conveniently, the two companies that antitrust department head
Delrahim lobbied for in the past - while the Federal Trade
Commission will have jurisdiction over Amazon and Facebook.
Google - An
integral part of the national security state?
Google could potentially also garner some protection or aid from the
U.S. National Security Agency (NSA).
According to an Aljazeera
report 41 published in 2014, emails reveal a cozy
relationship between Google and the NSA, with coordination occurring
at the highest levels.
Two years later, in March 2016, Wired reported 42 the
executive chairman of Google's parent company Alphabet and former
Google CEO, Eric Schmidt, had been chosen by the Pentagon to chair
its new Defense Innovation Advisory Board.
According to a Pentagon
press release: 43
"The board will seek to advise the department on areas that are
deeply familiar to Silicon Valley companies, such as rapid
prototyping, iterative product development, complex data analysis in
business decision making, the use of mobile and cloud applications,
and organizational information sharing."
Google is not what it seems
In his article, 44 "Google is not what it seems," Wikileaks founder Julian Assange also details,
"the special
relationship between Google, Hillary Clinton and the State
Department."
I recommend reading through this detailed and
comprehensive analysis for your own edification. The article is an
extract from his book, "When Google Met Wikileaks."
He writes in part:
"Google is 'different.' Google is 'visionary.' Google is 'the
future.' Google is 'more than just a company.' Google 'gives back to
the community.' Google is 'a force for good'…
The company's
reputation is seemingly unassailable. Google's colorful, playful
logo is imprinted on human retinas just under six billion times each
day, 2.1 trillion times a year - an opportunity for respondent
conditioning enjoyed by no other company in history.
Caught red-handed… making petabytes
of personal data available to the US intelligence community
through
the PRISM program, Google nevertheless continues to
coast on the goodwill generated by its 'don't be evil'
doublespeak...
Even anti-surveillance campaigners cannot help themselves, at once
condemning government spying but trying to alter Google's invasive
surveillance practices using appeasement strategies.
Nobody wants to
acknowledge that Google has grown big and bad. But it has.
Eric Schmidt's tenure as CEO saw Google integrate with the shadiest of US
power structures as it expanded into a geographically invasive mega-corporation.
But Google has always been comfortable with this
proximity.
Long before company founders Larry Page and
Sergey Brin hired
Schmidt in 2001, their initial research upon which Google was based
had been partly funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects
Agency (DARPA).
And even as Schmidt's Google developed an image as the overly
friendly giant of global tech, it was building a close relationship
with the intelligence community. In 2003 the US National Security
Agency (NSA) had already started systematically violating the
Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) under its director
General Michael Hayden.
These were the days of the 'Total Information Awareness' program.
Before PRISM was ever dreamed of… the NSA was already aiming to,
'collect it all, sniff it all, know it all, process it all, exploit
it all.'
During the same period, Google - whose publicly declared corporate
mission is to collect and 'organize the world's information and make
it universally accessible and useful' - was accepting NSA money to
the tune of $2 million to provide the agency with search tools for
its rapidly accreting hoard of stolen knowledge."
Assange also points out what he calls a "crucial detail" in the
media's reporting on the email correspondence between Schmidt,
Google co-founder Sergei Brin and NSA chief general
Keith Alexander:
"'Your insights as a key member of the Defense Industrial Base,'
Alexander wrote to Brin, 'are valuable to ensure ESF's [Enduring
Security Framework program] efforts have measurable impact'…
The Department of Homeland Security defines the Defense Industrial
Base as,
'the worldwide industrial complex that enables research and
development, as well as design, production, delivery, and
maintenance of military weapons systems, subsystems, and components
or parts, to meet U.S. military requirements'.
The Defense Industrial Base provides,
'products and services that are
essential to mobilize, deploy, and sustain military operations.'
Does it include regular commercial services purchased by the US
military?
No. The definition specifically excludes the purchase of regular
commercial services. Whatever makes Google a 'key member of the
Defense Industrial Base,' it is not recruitment campaigns pushed out
through Google AdWords or soldiers checking their Gmail…
Google's geopolitical aspirations are firmly enmeshed within the
foreign-policy agenda of the world's largest superpower.
As Google's
search and Internet service monopoly grows, and as it enlarges its
industrial surveillance cone to cover the majority of the world's
population... and racing to extend Internet access in the global
south, Google is steadily becoming the Internet for many people.
Its influence on the choices and behavior of the totality of
individual human beings translates to real power to influence the
course of history.
If the future of the
Internet is to be Google,
that should be of serious concern to people all over the world... for
whom the Internet embodies the promise of an alternative to US
cultural, economic, and strategic hegemony."
Decentralization is key - And it's coming
Just as
Larry Sanger realized a decentralized system is the best way to
create a new, more bias-resilient version of Wikipedia, 45
others have realized a decentralized Web is the answer to Google's
monopoly, growing censorship and rapidly deteriorating privacy
online.
A June 3, 2019 article 46 on Mediapost.com presents the
ideas of Sir Tim Berners-Lee, Vint Cerf and Brewster Kahle - three
early web inventors - who are actively trying to devise ways to,
"protect and rebuild the open nature of the web."
Berners-Lee, credited with inventing the
World Wide Web, had
originally envisioned it as an open source space.
Realizing how
private corporations have locked it down, he's now working on
another, decentralized, Internet solution. 47
As reported
by
Mediapost.com: 48
"'We demonstrated that the web had failed instead of served
humanity, as it was supposed to have done,' Berners-Lee told Vanity
Fair.
The web has,
'ended up producing - [through] no deliberate
action of the people who designed the platform - a large-scale
emergent phenomenon which is anti-human.'
So, they're out to fix it, working on what they call the Dweb. The
'd' in Dweb stands for distributed.
In distributed systems, no one
entity has control over the participation of any other entity.
Berners-Lee is building a platform called 'Solid,' designed to give
people control over their own data.
Other global projects also have the goal of taking take back the
public web.
This July 18-21, web
activists plan to convene at the Decentralized Web Summit in San
Francisco...
Last year's Dweb gathering convened more than 900 developers,
activists, artists, researchers, lawyers, and students.
Kahle opened
the gathering by reminding attendees that the web used to be a place
where everyone could play.
'Today, I no longer feel like a player, I feel like I'm being
played. Let's build a decentralized web, let's build a system we can
depend on, a system that doesn't feel creepy' he said..."
Boycott Google
and support decentralized initiatives
Why does Google and its allies fear Mercola.com (and other
"inconvenient" websites) and feel the need to
censor the information it is provided?
I believe the Wikipedia page
created about and held hostage by detractors offer strong
hints at the parties that would like to shut me up by shutting me
down.
In the end, it's going to come down to a battle between those
wanting to concentrate power against those trying to decentralize
it.
If we work together to boycott them, Google will crumble under
its own colossal weight.
How to find
Mercola.com articles moving forward
As mentioned in part 1 far above, you can
no longer get any of my articles using keyword searches only in a
Google-based search engine.
You can also see the impact over the
years in the graph below.

To find my articles, you have to add "Mercola.com" (or
"Bibliotecapleyades.net" if it is the case) to your search
term (example: "Mercola.com heart disease" or "Mercola.com Type 2
diabetes").
Even skipping the ".com" will minimize your search
results.
So, moving forward, here
are a few suggestions for how to stay connected:
-
Become a
subscriber to my newsletter and encourage your friends and
family to do the same. This is the easiest and safest way to
make sure you'll stay up to date on important health and
environmental issues.
NB:
Become a subscriber too, to
Biblioteca Pleyades newsletter.
-
If you have any
friends or relatives who are seriously interested in their
health, share important articles with them and encourage
them subscribe to our newsletter.
-
Nearly all major
search engines except
Yahoo! and
Bing use Google as their
primary engines, so if you use them, be sure to type mercola.com in your search query. This way, you will still
find our deeply buried content. Remember, relevant
Mercola.com articles will NOT show when you're using a
keyword search alone anymore.
-
Use the internal
Mercola.com search engine when searching for articles on my
site.
NB:
Use the internal
Biblioteca Pleyades search engine
when searching for articles in B. Pleyades.
Video
Sources and References
1 Wikipedia
Joseph Mercola
2 RationalWiki
Joseph Mercola
3 Telapost,
The June 4, 2019 Google broad core algorithm update
4, 5, 7, 12 Full
Measure August 21, 2016
6, 11, 13, 14 Sharylattkisson.com
May 25, 2019
8 Citizendium,
Why Citizendium?
9, 18 ANH.USA.org
September 7, 2010
10, 17, 45 150Sec.com
May 23, 2019
15 Age
of Autism DR. PAUL OFFIT SUED FOR INVASION OF PRIVACY IN
THE CIRCUIT COURT OF THE STATE OF OREGON FOR THE COUNTY
OF MULTNOMAH
16 Orange
County Register Corrections for April 18 2011
19 Business
Insider March 25, 2014
20 Change.org
March 23, 2014
21 Tech
Crunch January 22, 2019
22 Google
Blog January 22, 2019
23 The
Register June 6, 2016
24 New
York Times January 4, 2013
25 Music
Technology Policy August 9, 2016
26, 30 The
Verge June 11, 2019
27 The
Mercury News June 1, 2007
28, 29, 39, 40 New
York Times June 5, 2019
31 Public
Citizen, FTCs big tech revolving door problem, May 23,
2019
32, 33 Washington
Post August 30, 2017
34 Campaign
for Accountability July 11, 2017
35 The
Guardian July 12, 2017
36 Digit,
Don’t Be Evil
37 The
Wall Street Journal July 14, 2017
38 The
Times July 13, 2017
41 Aljazeera
May 6, 2014
42 Wired
March 2, 2016
43 Department
of Defense March 2, 2016
44 Wikileaks.org,
Google is not what it seems
46, 48 Mediapost.com
June 3, 2019
47 Forbes
June 12, 2019
49 Fast
Company, Inside DuckDuckGo
50 Startpage.com
51 Opera
Browser
52 ProtonMail
53 Digital
Trends April 28, 2017
|